由于很多教程编写的pass存在问题,自己又不会改 ,本系列教程目的是学习编写llvm pass 主要跟着llvm官网提供的教程来学习,官方提供的教程一个自制的llvm前端编程语言万花筒为例。
万花筒语言 – The Kaleidoscope Language
万花筒是一个允许定义函数,使用判断,数学等的程序语言,整个教程中,我们会拓展万花筒来支持 if/then/else 构建,循环,用户自定义操作符,一行命令接口的JIT 编译 ,调试信息等。
我们想让事情简单,所以在万花筒唯一的数据类型是64位的浮点类型(C语言中的double),所有的值默认都是双精度并且万花筒不需要定义。这样让万花筒非常友好,语法简单。例如一个Fibonacci number 计算的例子。
# Compute the x'th fibonacci number.
def fib(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
fib(x-1)+fib(x-2)
# This expression will compute the 40th number.
fib(40)
LLVM JIT 也让万花筒支持调用标准库函数 变得简单,这意味着你可以用’extern’ 关键词在你使用前来定义个函数。例如:
extern sin(arg);
extern cos(arg);
extern atan2(arg1 arg2);
atan2(sin(.4), cos(42))
更有趣的例子在第六章 我们写了一些万花筒的应用用来在不同的放大倍数来展现Mandelbrot 集合。
词法分析器 – Lexer
实现一个程序语言的时候,第一件事就是需要处理文本内容和意识到它在表达什么。传统实现方式是使用”Lexer” 词法分析器把输入分解成 “tokens” 。每个词法分析器返回的token 包括token码 和一些元数据。
// The lexer returns tokens [0-255] if it is an unknown character, otherwise one
// of these for known things.
enum Token {
tok_eof = -1,
// commands
tok_def = -2,
tok_extern = -3,
// primary
tok_identifier = -4,
tok_number = -5,
};
static std::string IdentifierStr; // Filled in if tok_identifier
static double NumVal; // Filled in if tok_number
通过词法分析器返回的每个token 会是某个Token 枚举值(Token enum values)或者是不知道(未定义)的字符像 “+” 就会返回它的Ascii值。如果当前的token是一个标识符(Token == -4),那么全局变量IdentifierStr就会标识符的名称。如果当前koken是数字,那么全局变量NumVal 就会保存它的值。我们因为简单使用全局变量,但是对于真正的语言实现并不是一个好的选择。
词法分析的真正实现是一个叫gettok的简单函数,gettok函数被调用时返回标准输入的下一个token。它定义的开始是:
// gettok - Return the next token from standard input.
static int gettok() {
static int LastChar = ' ';
// Skip any whitespace.
while (isspace(LastChar))
LastChar = getchar();
gettok 通过调用C函数getchar() 来从标准输入每次读取一个字符。它在识别出它们后就吃掉它们,并将最后读取但未处理的字符存储在LastChar中。它要做的第一件事是忽略令牌之间的空格。这是通过上面的循环完成的。
gettok要做的下一件事是识别标识符和特定的关键字像”def” , 万花筒通过它的循环来实现:
if (isalpha(LastChar)) { // identifier: [a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*
IdentifierStr = LastChar;
while (isalnum((LastChar = getchar())))
IdentifierStr += LastChar;
if (IdentifierStr == "def")
return tok_def;
if (IdentifierStr == "extern")
return tok_extern;
return tok_identifier;
}
注意,此代码在对标识符进行词法识别时会全局设置“ IdentifierStr”, 另外
…….自己看到第二章中间终于看不下去了 ,直接看代码才是我的风格。
#include "llvm/ADT/STLExtras.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Lexer
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// The lexer returns tokens [0-255] if it is an unknown character, otherwise one
// of these for known things.
enum Token {
tok_eof = -1,
// commands
tok_def = -2,
tok_extern = -3,
// primary
tok_identifier = -4,
tok_number = -5
};
static std::string IdentifierStr; // Filled in if tok_identifier
static double NumVal; // Filled in if tok_number
/// gettok - Return the next token from standard input.
//读取输入,标记token和对应的值。
static int gettok() {
static int LastChar = ' ';
// Skip any whitespace.
while (isspace(LastChar))
LastChar = getchar();
if (isalpha(LastChar)) { // identifier: [a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*
IdentifierStr = LastChar;
while (isalnum((LastChar = getchar())))
IdentifierStr += LastChar;
if (IdentifierStr == "def")
return tok_def;
if (IdentifierStr == "extern")
return tok_extern;
return tok_identifier;
}
if (isdigit(LastChar) || LastChar == '.') { // Number: [0-9.]+
std::string NumStr;
do {
NumStr += LastChar;
LastChar = getchar();
} while (isdigit(LastChar) || LastChar == '.');
NumVal = strtod(NumStr.c_str(), nullptr);
return tok_number;
}
if (LastChar == '#') {
// Comment until end of line.
do
LastChar = getchar();
while (LastChar != EOF && LastChar != '\n' && LastChar != '\r');
if (LastChar != EOF)
return gettok();
}
// Check for end of file. Don't eat the EOF.
if (LastChar == EOF)
return tok_eof;
// Otherwise, just return the character as its ascii value.
int ThisChar = LastChar;
LastChar = getchar();
return ThisChar;
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Abstract Syntax Tree (aka Parse Tree)
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
namespace {
/// ExprAST - Base class for all expression nodes.
class ExprAST {
public:
virtual ~ExprAST() = default;
};
/// NumberExprAST - Expression class for numeric literals like "1.0".
class NumberExprAST : public ExprAST {
double Val;
public:
NumberExprAST(double Val) : Val(Val) {}
};
/// VariableExprAST - Expression class for referencing a variable, like "a".
class VariableExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string Name;
public:
VariableExprAST(const std::string &Name) : Name(Name) {}
};
/// BinaryExprAST - Expression class for a binary operator.
class BinaryExprAST : public ExprAST {
char Op;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS, RHS;
public:
BinaryExprAST(char Op, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> RHS)
: Op(Op), LHS(std::move(LHS)), RHS(std::move(RHS)) {}
};
/// CallExprAST - Expression class for function calls.
class CallExprAST : public ExprAST {
std::string Callee;
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args;
public:
CallExprAST(const std::string &Callee,
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args)
: Callee(Callee), Args(std::move(Args)) {}
};
/// PrototypeAST - This class represents the "prototype" for a function,
/// which captures its name, and its argument names (thus implicitly the number
/// of arguments the function takes).
class PrototypeAST {
std::string Name;
std::vector<std::string> Args;
public:
PrototypeAST(const std::string &Name, std::vector<std::string> Args)
: Name(Name), Args(std::move(Args)) {}
const std::string &getName() const { return Name; }
};
/// FunctionAST - This class represents a function definition itself.
class FunctionAST {
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> Proto;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body;
public:
FunctionAST(std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> Proto,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> Body)
: Proto(std::move(Proto)), Body(std::move(Body)) {}
};
} // end anonymous namespace
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Parser
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
/// CurTok/getNextToken - Provide a simple token buffer. CurTok is the current
/// token the parser is looking at. getNextToken reads another token from the
/// lexer and updates CurTok with its results.
static int CurTok;
static int getNextToken() { return CurTok = gettok(); }
/// BinopPrecedence - This holds the precedence for each binary operator that is
/// defined.
static std::map<char, int> BinopPrecedence;
/// GetTokPrecedence - Get the precedence of the pending binary operator token.
static int GetTokPrecedence() {
if (!isascii(CurTok))
return -1;
// Make sure it's a declared binop.
int TokPrec = BinopPrecedence[CurTok];
if (TokPrec <= 0)
return -1;
return TokPrec;
}
/// LogError* - These are little helper functions for error handling.
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LogError(const char *Str) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", Str);
return nullptr;
}
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> LogErrorP(const char *Str) {
LogError(Str);
return nullptr;
}
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseExpression();
/// numberexpr ::= number
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseNumberExpr() {
auto Result = std::make_unique<NumberExprAST>(NumVal);
getNextToken(); // consume the number
return std::move(Result);
}
/// parenexpr ::= '(' expression ')'
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseParenExpr() {
getNextToken(); // eat (.
auto V = ParseExpression();
if (!V)
return nullptr;
if (CurTok != ')')
return LogError("expected ')'");
getNextToken(); // eat ).
return V;
}
/// identifierexpr
/// ::= identifier
/// ::= identifier '(' expression* ')'
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIdentifierExpr() {
std::string IdName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken(); // eat identifier.
if (CurTok != '(') // Simple variable ref.
return std::make_unique<VariableExprAST>(IdName);
// Call.
getNextToken(); // eat (
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> Args;
if (CurTok != ')') {
while (true) {
if (auto Arg = ParseExpression())
Args.push_back(std::move(Arg));
else
return nullptr;
if (CurTok == ')')
break;
if (CurTok != ',')
return LogError("Expected ')' or ',' in argument list");
getNextToken();
}
}
// Eat the ')'.
getNextToken();
return std::make_unique<CallExprAST>(IdName, std::move(Args));
}
/// primary
/// ::= identifierexpr
/// ::= numberexpr
/// ::= parenexpr
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (CurTok) {
default:
return LogError("unknown token when expecting an expression");
case tok_identifier:
return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case tok_number:
return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(':
return ParseParenExpr();
}
}
/// binoprhs
/// ::= ('+' primary)*
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseBinOpRHS(int ExprPrec,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> LHS) {
// If this is a binop, find its precedence.
while (true) {
int TokPrec = GetTokPrecedence();
// If this is a binop that binds at least as tightly as the current binop,
// consume it, otherwise we are done.
if (TokPrec < ExprPrec)
return LHS;
// Okay, we know this is a binop.
int BinOp = CurTok;
getNextToken(); // eat binop
// Parse the primary expression after the binary operator.
auto RHS = ParsePrimary();
if (!RHS)
return nullptr;
// If BinOp binds less tightly with RHS than the operator after RHS, let
// the pending operator take RHS as its LHS.
int NextPrec = GetTokPrecedence();
if (TokPrec < NextPrec) {
RHS = ParseBinOpRHS(TokPrec + 1, std::move(RHS));
if (!RHS)
return nullptr;
}
// Merge LHS/RHS.
LHS = std::make_unique<BinaryExprAST>(BinOp, std::move(LHS),
std::move(RHS));
}
}
/// expression
/// ::= primary binoprhs
///
static std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseExpression() {
auto LHS = ParsePrimary();
if (!LHS)
return nullptr;
return ParseBinOpRHS(0, std::move(LHS));
}
/// prototype
/// ::= id '(' id* ')'
static std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParsePrototype() {
if (CurTok != tok_identifier)
return LogErrorP("Expected function name in prototype");
std::string FnName = IdentifierStr;
getNextToken();
if (CurTok != '(')
return LogErrorP("Expected '(' in prototype");
std::vector<std::string> ArgNames;
while (getNextToken() == tok_identifier)
ArgNames.push_back(IdentifierStr);
if (CurTok != ')')
return LogErrorP("Expected ')' in prototype");
// success.
getNextToken(); // eat ')'.
return std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>(FnName, std::move(ArgNames));
}
/// definition ::= 'def' prototype expression
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseDefinition() {
fprintf(stdout,"[+] print %s\n" ,IdentifierStr.c_str());
// std::cout << IdentifierStr <<std::endl;
getNextToken(); // eat def.
fprintf(stdout,"[+] print %s\n" ,IdentifierStr.c_str());
auto Proto = ParsePrototype();
if (!Proto)
return nullptr;
if (auto E = ParseExpression())
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(Proto), std::move(E));
return nullptr;
}
/// toplevelexpr ::= expression
static std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseTopLevelExpr() {
if (auto E = ParseExpression()) {
// Make an anonymous proto.
auto Proto = std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>("__anon_expr",
std::vector<std::string>());
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(Proto), std::move(E));
}
return nullptr;
}
/// external ::= 'extern' prototype
static std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParseExtern() {
getNextToken(); // eat extern.
return ParsePrototype();
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Top-Level parsing
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
static void HandleDefinition() {
if (ParseDefinition()) {
fprintf(stderr, "Parsed a function definition.\n");
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
static void HandleExtern() {
if (ParseExtern()) {
fprintf(stderr, "Parsed an extern\n");
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
static void HandleTopLevelExpression() {
// Evaluate a top-level expression into an anonymous function.
if (ParseTopLevelExpr()) {
fprintf(stderr, "Parsed a top-level expr\n");
} else {
// Skip token for error recovery.
getNextToken();
}
}
/// top ::= definition | external | expression | ';'
static void MainLoop() {
while (true) {
fprintf(stderr, "ready> ");
switch (CurTok) {
case tok_eof:
return;
case ';': // ignore top-level semicolons.
getNextToken();
break;
case tok_def:
HandleDefinition();
break;
case tok_extern:
HandleExtern();
break;
default:
HandleTopLevelExpression();
break;
}
}
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Main driver code.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
int main() {
// Install standard binary operators.
// 1 is lowest precedence.
BinopPrecedence['<'] = 10;
BinopPrecedence['+'] = 20;
BinopPrecedence['-'] = 20;
BinopPrecedence['*'] = 40; // highest.
// Prime the first token.
fprintf(stderr, "ready> ");
getNextToken();
// Run the main "interpreter loop" now.
MainLoop();
return 0;
}
编译命令(自己改下):$LLVM_HOME/bin/clang++ -g -O3 toy.cpp -std=c++14 llvm-config --ldflags --libs -lpthread -I$LLVM_HOME/include -ldl -lz -ltinfo
什么是抽象语法树,个人简单理解就是用一颗树来存一个表达式或者说语法块(不一定正确),表达式越复杂树越复杂。通过直接看代码发现万花筒支持定义使用了四种token ,def extern identifier number,用于词法分析,首先分析语句,可以是标识符、数字或者表达式。
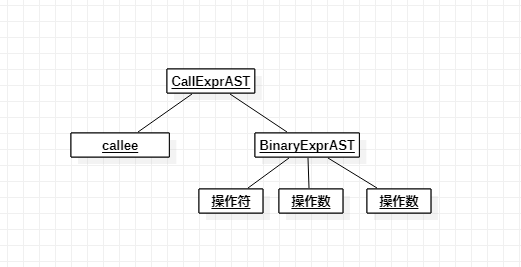
以A(1+1)为例子分析:
程序执行流程为 HandleTopLevelExpression -> ParseTopLevelExpr -> ParseExpression->ParsePrimary -> ParseIdentifierExpr ->ParseExpression->ParsePrimary ->ParseNumberExpr ->ParseBinOpRHS- > ParsePrimary ->ParseNumberExpr ->ParseBinOpRHS(一次迭代) 先看程序执行不关心语法树组成。将A(1+1)看作一个表达式,A为identifier 再将1+1 看作一个表达式,解析 1 后遇到”+” 后判断操作符优先级后解析下一个token,此时下一个token为1 ,在判断再下一个token的优先级,因为是”)”返回”-1″,然后将”1 + 1″表达式合并再返回,层层返回回到ParseIDentifierExpr ,成为”A”标识符的参数,返回合成的语法树,表达式解析结束。
然后我们再看其中使用了哪些语法树,在ParseIdentifierExpr会返回一个CallExprAST 语法树,CallExprAST语法树初始化时参数为函数名称callee 和BinaryExprAST 语法树,在这个例子中,使用的类ParseNumberExpr该类仅有一个成员表示这个数值,嘿嘿 其实再看一眼就会发现”1+1″其实不是返回ParseNumberExpr ,由于遇到”+” 且后面的token合法,所以返回了一个BinaryExprAST语法树,最终生成的树就是:
https://llvm.org/docs/tutorial/MyFirstLanguageFrontend/index.html MyfirstLanguagefrontend
其中的小插曲,打印std::string 报了个错,内容忘了 就是缺少了stdlibc++ 的调试信息包,装一下就好。
sudo apt install libstdc++6-8-dbg
0 条评论