内存修改实现
Env
ubuntu18
introduction
做反外挂时, 发现开启进程自保护后,GG修改器同样可以对应用的内存进行扫描和修改 ,判断修改器并非使用ptrace完成内存修改操作, 所以引入两一种内存修改的方法。
proc/[pid]/mem
Linux manual page 对/proc 目录的介绍,
The proc filesystem is a pseudo-filesystem which provides an interface to kernel data structures. It is commonly mounted at /proc. Typically, it is mounted automatically by the system,
其中有个特殊的目录/proc/[pid]/mem。
This file can be used to access the pages of a process's memory through open(2), read(2), and lseek(2).
Permission to access this file is governed by a ptrace access mode PTRACE_MODE_ATTACH_FSCREDS check; see ptrace(2).
我们可以通过访问这个文件来访问相应进程的内存空间,并且通过修改文件相应偏移的数据来实现按相应进程空间的数据。
process_vm_readv/writev
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/process_vm_readv.2.html , 官方介绍。
但是该接口受进程页权限管理。不可写的内存,不能通过process_vm_writev写入,同理readv。
experience
待修改程序源码, 输出当前进程pid , 空间地址和其中的字符串。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
char buf[200] = {"mcl hello world 123 "};
while (1)
{
/* code */
printf("pid = %d , buf addr: %p , value = %s\n", getpid() , &buf , buf);
sleep(5);
}
return 0;
}
内存修改器代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <error.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc , char ** argv){
char buffer[50];
char * despath = (char * )malloc( sizeof(char)*( sizeof(argv[1]) + sizeof("/proc//mem")) );
sprintf(despath , "/proc/%s/mem",argv[1]);
printf("despath %s\n" , despath);
long long offset = 0x7fff660fb9b0;
printf("offset %p\n" , offset);
int file = open(despath , O_RDWR );
if(file <= 0){
printf("fopen error %s\n",strerror(errno));
exit(0);
}
else
printf("fopen succuessful\n");
int err;
printf("lseek %d\n" ,file);
if(lseek(file , offset ,SEEK_SET) == -1){
printf("fseek error %s \n" ,strerror(errno));
}
int lenth;
if(( lenth = read(file , buffer , sizeof(buffer)) )> 0 )
printf("buffer %s \n" , buffer);
else
{
printf("lenth %d\n" , lenth);
}
lseek(file , offset ,SEEK_SET);
write(file , "you must be changed one more time\n" , sizeof("you must be changed one more time\n"));
close(file);
return 0;
}
运行两个程序:
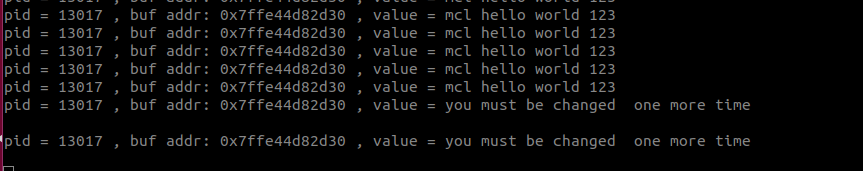
检测
inotify机制
monitoring filesystem events
该机制提供对文件系统的监控,包括但不限于 修改 , 访问 , 打开,关闭 ,移动。
inotify 机制更多相关内容参见reference。
检测代码
#include <errno.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/inotify.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc , char ** argv){
char buf[4096];
int fd = inotify_init();
int ret;
int PID = atoi(argv[1]);
char * memmappath = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * ( sizeof(int)+sizeof("/proc//pagemap") ) );
char * mempath = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * ( sizeof(int) + sizeof("/proc//mem") ) );
fd_set readfds;
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
FD_SET(fd,&readfds);
sprintf(memmappath , "/proc/%d/pagemap" ,PID);
sprintf(mempath , "/proc/%d/mem",PID);
printf("mempath %s\n",mempath);
printf("memmappath %s \n",memmappath);
inotify_add_watch(fd,memmappath,IN_ALL_EVENTS);
inotify_add_watch(fd,mempath,IN_ALL_EVENTS);
for(;;){
ret = select(fd + 1, &readfds, 0, 0, 0);
if(ret){
int length = read(fd, buf ,4096);
for(int i = 0 ; i < length ; i+=sizeof(struct inotify_event))
{
struct inotify_event * e = (struct inotify_event *)&buf[i];
printf("%s [%d] be touch %x\n", e->name, e->len, e->mask);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
测试效果:
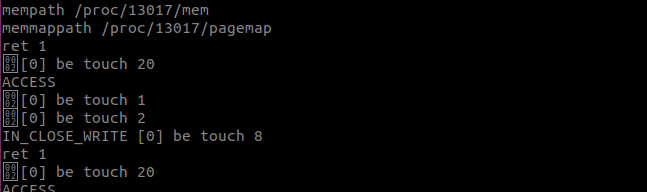
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/proc.5.html Linux manual page
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/inotify.7.html inotify相关
0 条评论