起因
使用ptrace来注入进程 ,detach以后出现了EIP-2的现象,猜测这个eip-2 时为了重新进入系统调用,该篇文章为了验证这个过程。
从中断到系统调用到执行ptrace 分析。
环境
内核版本: 4.10.1
ubuntu 18
编译, 调试过程参考该目录下其他文档。
中断、异常和系统调用
中断被定义为一个事件,可以改变CPU指令顺序 .异常由程序错误产生或者是由内核必须处理的异常条件产生的(深入理解linux内核).
中断描述符表
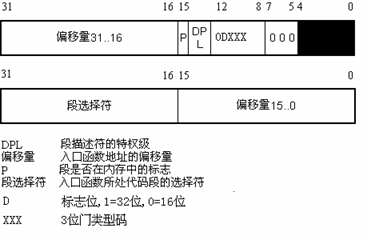
https://book.aikaiyuan.com/kernel/3.1.4.htm
主要讲四个字段,门类型 , 中断号 , 跳转地址 DPI
intel提供三种门类型:
- 任务门
- 中断门
- 陷阱门
实际上linux提供了五种门:
- 系统门
- 系统中断门
系统调用
简单说就是中断号为0x80 的软中断. 入口函数保存现场,调用调用号的地址,结束后还原现场。
中断到系统调用的过程
内核在启动时,在trap_init过程中对可编程中断控制器(pic)进行初始化确定中断矢量调用的地址。
void __init trap_init(void)
{
...
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_32
printk("CONFIG_X86_32");
set_system_intr_gate(IA32_SYSCALL_VECTOR, entry_INT80_32);
set_bit(IA32_SYSCALL_VECTOR, used_vectors);
#endif
...
}
初始化过程结束后,当这发生中断矢量为0x80时,就会跳转到entry_INT80_compat入口函数去,这个跳转的过程由可编程中断控制器完成。set_system_intr_gate 为linux提供的系统中断门,内核提供给linux用户态的接口,表示用户态程序使用该中断号可以进入到内核态。中断中断门 除了0x80 以为还有0x3 。
ENTRY(entry_INT80_32)
ASM_CLAC
pushl %eax /* pt_regs->orig_ax */
SAVE_ALL pt_regs_ax=$-ENOSYS /* save rest */
/*
* User mode is traced as though IRQs are on, and the interrupt gate
* turned them off.
*/
TRACE_IRQS_OFF
movl %esp, %eax
call do_int80_syscall_32 #
.Lsyscall_32_done:
跳转到系统调用处理函数,
/* Handles int $0x80 */
__visible void do_int80_syscall_32(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
enter_from_user_mode();
local_irq_enable(); //启用中断
do_syscall_32_irqs_on(regs); //重点
}
static __always_inline void do_syscall_32_irqs_on(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct thread_info *ti = current_thread_info();
unsigned int nr = (unsigned int)regs->orig_ax; //获取系统调用号
#ifdef CONFIG_IA32_EMULATION
current->thread.status |= TS_COMPAT;
#endif
if (READ_ONCE(ti->flags) & _TIF_WORK_SYSCALL_ENTRY) {
/*
* Subtlety here: if ptrace pokes something larger than
* 2^32-1 into orig_ax, this truncates it. This may or
* may not be necessary, but it matches the old asm
* behavior.
*/
nr = syscall_trace_enter(regs);
}
if (likely(nr < IA32_NR_syscalls)) {
/*
* It's possible that a 32-bit syscall implementation
* takes a 64-bit parameter but nonetheless assumes that
* the high bits are zero. Make sure we zero-extend all
* of the args.
*/
// 函数指针表 ,通过nr指到调用的地址。
regs->ax = ia32_sys_call_table[nr](
(unsigned int)regs->bx, (unsigned int)regs->cx,
(unsigned int)regs->dx, (unsigned int)regs->si,
(unsigned int)regs->di, (unsigned int)regs->bp); //保存参数,执行系统调用
}
syscall_return_slowpath(regs);
}
ptrace过程
几个关键函数或者宏
/*
写者也可以用它来获得锁,与write_lock不同的是,该宏还同时失效了本地中断。该宏与write_lock_irqsave的不同之处是,它没有保存标志寄存器。
*/
#define write_lock_irq(lock) \
do { \
local_irq_disable(); \
preempt_disable(); \
_raw_write_lock(lock); \
} while (0)
/*
*/
#define write_unlock_irq(lock) \
do { \
_raw_write_unlock(lock); \
local_irq_enable(); \
preempt_enable(); \
} while (0)
/*
将其放会到原父进程之下,并且从ptrace list 列表中移除
*/
void __ptrace_unlink(task_t *child)
{
if (!child->ptrace)
BUG();
child->ptrace = 0;
if (list_empty(&child->ptrace_list))
return;
list_del_init(&child->ptrace_list);
REMOVE_LINKS(child);
child->parent = child->real_parent;
SET_LINKS(child);
}
Detach 过程
int ptrace_detach(struct task_struct *child, unsigned int data)
{
if ((unsigned long) data > _NSIG)
return -EIO;
/* Architecture-specific hardware disable .. */
ptrace_disable(child);
/* .. re-parent .. */
child->exit_code = data;
write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
__ptrace_unlink(child);
/* .. and wake it up. */
if (child->state != TASK_ZOMBIE)
wake_up_process(child);
write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
return 0;
}
已知了其他函数的作用,我们就把重心放在wake_up_process() 上。wake_up_process 调用了try_to_wake_up() 函数过程。
wake_up_process() 调用try_to_wake_up(),try_wake_up() 函数位于kernel/sched.c
static int try_to_wake_up(task_t * p, unsigned int state, int sync)
{
unsigned long flags;
int success = 0;
long old_state;
runqueue_t *rq;
repeat_lock_task:
//禁止本地中断
rq = task_rq_lock(p, &flags);
old_state = p->state;
if (old_state & state) {
//如果p->array字段不等于NULL,那么进程已经属于某个运行队列
if (!p->array) {
/*
* Fast-migrate the task if it's not running or runnable
* currently. Do not violate hard affinity.
*/
if (unlikely(sync && !task_running(rq, p) &&
(task_cpu(p) != smp_processor_id()) &&
cpu_isset(smp_processor_id(), p->cpus_allowed))) {
set_task_cpu(p, smp_processor_id());
task_rq_unlock(rq, &flags);
goto repeat_lock_task;
}
//进程处于不可中断状态。
if (old_state == TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE){
rq->nr_uninterruptible--;
/*
* Tasks on involuntary sleep don't earn
* sleep_avg beyond just interactive state.
*/
p->activated = -1;
}
if (sync && (task_cpu(p) == smp_processor_id()))
__activate_task(p, rq);
else {
activate_task(p, rq);
if (TASK_PREEMPTS_CURR(p, rq))
resched_task(rq->curr);
}
success = 1;
}
p->state = TASK_RUNNING;
}
task_rq_unlock(rq, &flags);
return success;
}
调试过程中,排除其他函数,定位到resched_task() 函数,过程涉及到进程切换,当前水平不够,学习Task_struct后再来尝试。
https://blog.csdn.net/hq815601489/article/details/80009791 Linux系统调用:使用int 0x80
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_33850890/article/details/92823320 Linux系统调用与ptrace分析
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-synch/part2/index.html Linux 内核的同步机制
http://abcdxyzk.github.io/blog/2015/02/11/kernel-sched-trywakeup/ try_to_wake_up分析
0 条评论